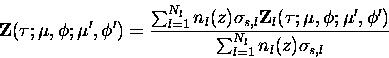 |
(7.11) |
The model atmosphere will, in general, contain both Rayleigh and several
different Mie scatterers. Under these circumstances, the effective phase
matrix is then a weighted average of each scatterer's phase matrix
with its extinction. In general, the atmosphere is inhomogeneous so the
effective phase matrix is height dependent. For Nl
different types of scatterers (Rayleigh or Mie),
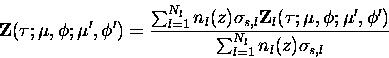 |
(7.11) |