
ESS5
Prof.
Jin-Yi Yu
–Rain is
associated with warm clouds exclusively and cool clouds when surface temperatures are above freezing
–Rainshowers are episodic precipitation events associated with convective activity and cumulus clouds
•Drops tend to be large and widely spaced to begin, then smaller
drops become more
prolific
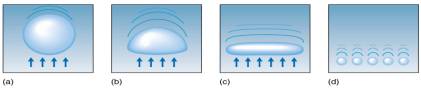
–Raindrop Shape begins as spherical
•As frictional drag
increases, changes to a mushroom shape
•Drops eventually
flatten
•Drops split when frictional drag overcomes the surface tension
of water
•Splitting ensures a maximum drop size of about 5 mm and the continuation of the collision-coalescence process
Rain