ESS227
Prof. Jin-Yi Yu
Potential
Temperature (θ)
•For an ideal gas
undergoing an adiabatic process
(i.e., a reversible process in
which no heat is exchanged with the surroundings; J=0), the first law of thermodynamics can be written in
differential form as:
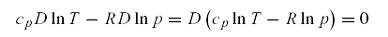
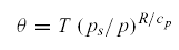
•Thus,
every air parcel has a unique value of potential temperature, and this value
is conserved for dry adiabatic motion.
•Because
synoptic scale motions are approximately adiabatic outside regions of
active precipitation, θ is
a quasi-conserved quantity for such motions.
•Thus,
for reversible processes, fractional potential temperature changes are indeed
proportional to entropy changes.
•A
parcel that conserves entropy following the motion must move along an isentropic (constant θ) surface.
è
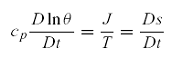
è